Use Case Library Glossary
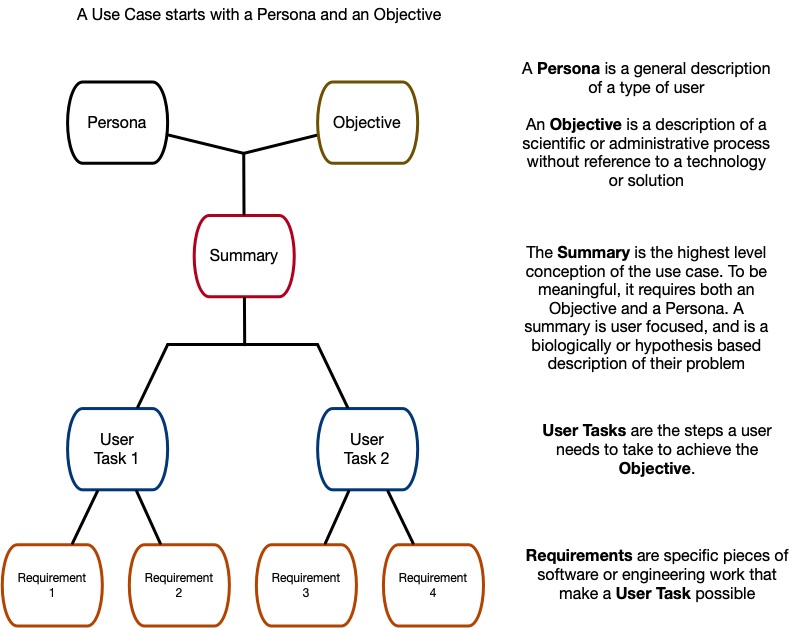
A Use Case consists of an Objective and a Persona - a person who can have an Objective. These are combined into a summary of specific use cases for the CFDE, which can be achieved by a series of user tasks. Each User Task is a single step in the user's workflow. The technical infrastructure required to enable a User Task are its Requirements. In most cases, what appears to the user as a single step actually is a multi-step process to the computer doing the work, so any given User Task will likely have many Requirements. Both user tasks and requirements can be shared across Use Cases.
Overview
Definitions
Objective
A description of a scientific process, told without reference to a specific technology solution. Focuses on resources required, method(s) followed, and outcome(s) targeted. Can be validated with scientific stakeholders.
Persona
A type of user who will appear in the epics and stories that follow.
Summary
A high-level, non-technical description of an entire Use Case. The user in each summary has a name, a scientific or administrative problem, and both proximate and ultimate goals. The focus is on the problem and what is generally needed to solve it.
User Task
A story, told from the user's perspective that captures a concrete step in a users interactions with tools (e.g. software solutions) in the service of achieving the scientific objective. Must be written in terms that are meaningful to the user, from their perspective. This can be thought of as one in a series of medium scale tasks that must be completed to answer the question posed in the scientific objective. The list of User Task in a Use Case should cover everything the user needs to achieve their goal, even interactions that don't involve the software or data from the Common Fund.
Requirement
A well-scoped and defined piece of software or data engineering work that is needed to support a User Task. These should be small tasks that can be verified with engineering teams (Did we deliver it? Yes or no.) A single requirement might be important for any number of different User Tasks, and various collections of Requirements can be grouped to support different User Tasks.